Precision is a measure of consistency or agreement between scores and concerns the degree to which errors of measurement affect test scores.
In Classical Test Theory, an observed score on a test can be considered an additive function of two values: the true score and measurement error. The true score is the unobserved quantity that one actually wants to measure, while measurement error is defined as random error that is unrelated to the true score but taints its measurement. The more measurement error there is, the less an observed score will align to its corresponding true score. Thus, the more measurement error there is, the less precisely a true score is measured.
There are many ways in which precision can be measured. In traditional test theory, precision is measured by a reliability coefficient, which is the ratio of true score variance to observed score variance (Lord & Novick, 1968) (See Figure 1).
Figure 1

Because true score variance can be computed as the difference between observed score variance and error variance, classical reliability can be represented as seen in Figure 2.
Figure 2

Item Response Theory (IRT)
Item Response Theory (IRT) provides a means of estimating reliability that operates on the item characteristics and the individual pattern of responses given by examinees to items within a test. The IRT analogue to classical reliability is called marginal reliability, and operates on the variance of the theta scores and the average of the expected error variance (Sireci, Thissen, & Wainer, 1991) (Figure 3).
Figure 3

If it can be safely assumed that theta is distributed N(0,1), then marginal reliability can be measured as seen in Figure 4.
When sample sizes are large, the average of the expected error variance can be computed by averaging the variance of the estimated posterior distributions across individuals. In the reliabilities reported below, the posterior standard deviation (PSD) for individual i was estimated using the methodology given in Bock and Mislevy (1982) (Figures 5 and 6).
Figure 4

Figure 5
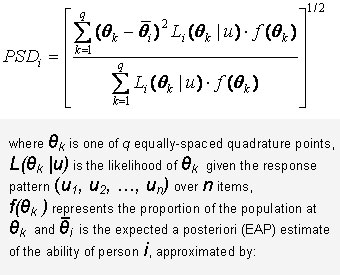
Figure 6
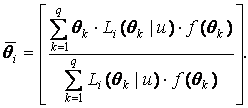
ASVAB Reliabilities
For each ASVAB subtest, the equation shown in Figure 6 was used to compute EAP ability estimates The equation shown in Figure 5 was then used to compute PSDs (using the EAP ability estimates, and assuming a N(0,1) population distribution). The average of the squared PSDs was then computed over applicants and substituted into the equation shown in Figure 4 to compute subtest reliability.
For AFQT scores, reliability was computed using the methodology for computing composite reliabilities reported in Gulliksen (1987; pg. 346-347, Equation 74).
For the CAT-ASVAB, the sample used to calculate the reliabilities consisted of applicants from the 2019 fiscal year (FY2019: October 1, 2018–September 30, 2019). For the P&P-ASVAB, the sample consisted of applicants from FY2011 through FY2019. This large range of years was used because the number of applicants taking the P&P-ASVAB has dramatically decreased over the last decade. Thus, to have a sample size similar to that of the CAT-ASVAB, 9 years’ worth of P&P-ASVAB data were required.
Reliability estimates were computed over all applicants, and by gender (Male, Female), ethnic group (Hispanic, Non-Hispanic), and race (American-Indian/Alaska Native, Asian, Black/African-American, Native Hawaiian/other Pacific Islander, White/Caucasian).
The sample sizes used to compute the reliability estimates across subtests and AFQT scores are given in the table below.
| Sample Sizes Used to Compute ASVAB Reliability & SEM Estimates | ||
|---|---|---|
| 2011–2019 | 2019 | |
| Group | P&P | CAT |
| All | 261,621 | 307,276 |
| Male
Female |
195,188
66,427 |
229,939
78,032 |
| Hispanic
Non-Hispanic |
33,572
210,628 |
67,852
239,323 |
| American-Indian
Asian Black Pacific Islander White |
2,978
9,272 64,398 4,061 159,670 |
2,416
14,434 73,039 1,946 206,341 |
The estimated reliabilities for AFQT scores and the subtests that comprise AFQT scores are reported in the table below.
Learn more about: AFQT Scores | ASVAB Subtests
| Estimated Reliabilities for AFQT Scores & the AFQT Subtests | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFQT | AR | WK | PC | MK | ||||||
| Group | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT |
| All | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.92 | 0.74 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.93 |
| Male Female |
0.94 0.94 |
0.97 0.97 |
0.87 0.86 |
0.91 0.91 |
0.88 0.88 |
0.92 0.92 |
0.74 0.75 |
0.85 0.86 |
0.86 0.86 |
0.93 0.93 |
| Hispanic Non-Hispanic |
0.94 0.94 |
0.96 0.97 |
0.87 0.87 |
0.91 0.91 |
0.88 0.88 |
0.92 0.93 |
0.74 0.74 |
0.86 0.85 |
0.86 0.86 |
0.93 0.93 |
| American-Indian Asian Black Pacific Islander White |
0.94 0.94 0.94 0.94 0.94 |
0.97 0.96 0.96 0.97 0.97 |
0.87 0.85 0.85 0.83 0.88 |
0.91 0.91 0.91 0.91 0.91 |
0.88 0.88 0.89 0.88 0.88 |
0.92 0.91 0.92 0.92 0.93 |
0.74 0.75 0.76 0.76 0.73 |
0.86 0.86 0.86 0.86 0.85 |
0.86 0.85 0.85 0.84 0.86 |
0.93 0.92 0.92 0.92 0.93 |
The estimated reliabilities for the remaining ASVAB subtests are given in the table below. Note that AI and SI are administered as separate subtests in CAT-ASVAB but are combined into one single score (labeled AS). AI and SI are combined into one single subtest (AS) in P&P-ASVAB. Therefore, reliability estimates for AS are reported for P&P-ASVAB but are not available for CAT-ASVAB.
| Estimated Reliabilities for the Non-AFQT Subtests | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS | EI | AI | SI | AS | MC | AO | ||||||||
| Group | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT |
| All | 0.81 | 0.87 | 0.71 | 0.86 | n/a | 0.85 | n/a | 0.82 | 0.79 | n/a | 0.79 | 0.84 | 0.83 | 0.81 |
| Male Female |
0.81 0.80 |
0.87 0.86 |
0.72 0.68 |
0.86 0.83 |
n/a n/a |
0.86 0.81 |
n/a n/a |
0.83 0.81 |
0.81 0.73 |
n/a n/a |
0.80 0.77 |
0.84 0.83 |
0.83 0.84 |
0.81 0.82 |
| Hispanic Non-Hispanic |
0.80 0.81 |
0.86 0.87 |
0.70 0.71 |
0.85 0.86 |
n/a n/a |
0.84 0.85 |
n/a n/a |
0.81 0.83 |
0.77 0.80 |
n/a n/a |
0.79 0.79 |
0.84 0.84 |
0.83 0.83 |
0.82 0.81 |
| American-Indian Asian Black Pacific Islander White |
0.81 0.78 0.79 0.77 0.82 |
0.87 0.86 0.85 0.86 0.87 |
0.72 0.67 0.69 0.67 0.72 |
0.86 0.85 0.84 0.85 0.86 |
n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a |
0.85 0.83 0.82 0.84 0.86 |
n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a |
0.83 0.81 0.80 0.82 0.83 |
0.81 0.74 0.73 0.75 0.82 |
n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a |
0.80 0.78 0.77 0.77 0.81 |
0.84 0.84 0.83 0.84 0.84 |
0.83 0.83 0.86 0.85 0.82 |
0.81 0.80 0.84 0.81 0.81 |
ASVAB Standard Errors of Measurement
The standard error of measurement (SEM) provides an alternate way of summarizing the amount of error or inconsistency in test scores. Figure 7 shows how this is computed, where ![]() is the observed score standard deviation for test x. Thus, the SEM is simply a function of two values: the standard deviation of the test and the reliability of the test. The higher the reliability of the test, the smaller the SEM, and the more precise the test is. If the measurement error is normally distributed and the reported scores are unbiased, then the true scores for approximately 68% of the applicants would fall in the interval created by adding and subtracting one SEM from their reported score.
is the observed score standard deviation for test x. Thus, the SEM is simply a function of two values: the standard deviation of the test and the reliability of the test. The higher the reliability of the test, the smaller the SEM, and the more precise the test is. If the measurement error is normally distributed and the reported scores are unbiased, then the true scores for approximately 68% of the applicants would fall in the interval created by adding and subtracting one SEM from their reported score.
Figure 7
The SEM of each ASVAB subtest and AFQT score was computed over all applicants, and by gender (Male, Female), ethnic group (Hispanic, Non-Hispanic), and race (American-Indian/Alaska Native, Asian, Black/African-American, Native Hawaiian/other Pacific Islander, White/Caucasian). The samples were the same as were used for the reliability analyses.
The SEMs for AFQT scores and the subtests that comprise AFQT scores are reported in the table below.
| Estimated Standard Errors of Measurement for AFQT Scores & AFQT Subtests | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFQT | AR | WK | PC | MK | ||||||
| Group | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT |
| All | 5.87 | 4.39 | 3.02 | 2.61 | 2.88 | 2.33 | 3.82 | 2.88 | 2.85 | 2.01 |
| Male Female |
5.93 5.61 |
4.38 4.27 |
3.02 2.88 |
2.58 2.55 |
2.88 2.85 |
2.32 2.28 |
3.89 3.60 |
2.94 2.66 |
2.91 2.66 |
2.03 1.95 |
| Hispanic Non-Hispanic |
5.56 5.90 |
4.33 4.39 |
2.76 3.03 |
2.48 2.64 |
2.88 2.86 |
2.40 2.28 |
3.69 3.84 |
2.78 2.89 |
2.76 2.85 |
2.00 2.01 |
| American-Indian Asian Black Pacific Islander White |
5.77 6.65 5.38 6.20 5.62 |
4.14 4.93 4.25 4.43 4.22 |
2.93 3.76 2.85 3.66 2.78 |
2.35 2.80 2.56 2.69 2.47 |
2.74 3.64 2.58 3.62 3.67 |
2.14 3.13 2.30 2.35 2.20 |
3.70 4.49 3.56 4.40 2.77 |
2.65 3.14 2.65 2.75 2.85 |
2.87 3.23 2.76 3.18 3.49 |
1.90 2.17 2.07 2.17 1.93 |
The SEMs for the remaining ASVAB subtests are given in the table below. Note that the SEM computations for AI and SI are based on the observed standard deviation of the AS score, since separate scores are not reported for AI and SI.
| Estimated Standard Errors of Measurement for the Non-AFQT Subtests | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS | EI | AI | SI | AS | MC | AO | ||||||||
| Group | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT | P&P | CAT |
| All | 3.82 | 3.26 | 4.96 | 3.59 | n/a | 3.50 | n/a | 3.74 | 4.20 | n/a | 3.98 | 3.51 | 3.38 | 3.61 |
| Male Female |
3.82 3.53 |
3.20 3.13 |
4.82 4.42 |
3.45 3.27 |
n/a n/a |
3.31 2.92 |
n/a n/a |
3.61 2.97 |
3.00 3.32 |
n/a n/a |
3.87 3.55 |
3.45 3.07 |
3.43 3.19 |
3.65 3.48 |
| Hispanic Non-Hispanic |
3.65 3.82 |
3.18 3.24 |
4.72 4.96 |
3.52 3.57 |
n/a n/a |
3.21 3.53 |
n/a n/a |
3.42 3.77 |
3.86 4.20 |
n/a n/a |
3.61 4.01 |
3.18 3.57 |
3.21 3.40 |
3.39 3.67 |
| American-Indian Asian Black Pacific Islander White |
3.69 4.74 3.45 4.53 3.49 |
2.99 3.89 3.14 3.17 3.04 |
4.67 5.65 4.56 5.04 4.61 |
3.36 4.08 3.47 3.52 3.35 |
n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a |
3.23 3.39 3.01 3.32 3.35 |
n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a |
3.43 3.61 3.12 3.50 3.57 |
3.82 4.03 3.51 4.04 3.80 |
n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a |
3.61 3.99 3.51 3.92 3.66 |
3.13 3.56 3.11 3.24 3.23 |
3.15 3.56 3.16 3.45 3.23 |
3.38 3.53 3.53 3.47 3.47 |


